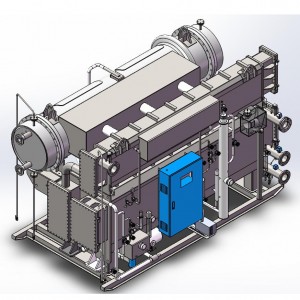
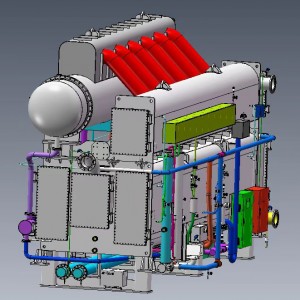
Products
Two Step Absorption Chiller
2.1 Working Principle
This unit consists of multiple circulating systems. Due to the low pressure within the evaporator, refrigerant water is pumped by the refrigerant pump and sprayed onto the evaporator tube. It absorbs heat from the chilled water in the tubes, causing it to evaporate and thereby lowering the temperature of the chilled water, thus achieving the refrigeration effect.
The refrigerant steam generated by the evaporator enters the low-temperature absorber. The concentrated solution in the absorber absorbs the refrigerant steam, transforming into a dilute solution. This dilute solution is pumped by the HTG pump, heated through a high temp. heat exchanger, and then enters the HTG. Within the HTG, the dilute solution is heated to boiling by the working hot water, producing refrigerant steam and concentrating the dilute solution into concentrated solution. The concentrated solution is cooled in a heat exchanger before returning to the low-temperature absorber. Then, it is further cooled by cooling water and continues absorbing refrigerant steam from the evaporator.
Refrigerant steam generated in the HTG enters the high-temperature absorber, where it is absorbed by the concentrated solution to form dilute solution. This dilute solution is pumped by LTG pump, heated in heat exchanger, and then enters the LTG. In the LTG, the dilute solution is heated to boiling by working hot water, producing refrigerant steam and concentrating the dilute solution into concentrated solution. The concentrated solution is cooled in a heat exchanger before returning to the high-temperature absorber. Then, it is further cooled by circulating cooling water and continues to absorb refrigerant steam from the HTG.
The refrigerant steam generated in the LTG is cooled by chilled water in the condenser, condensing into refrigerant water. This water flows through U-type tubes into the evaporator water plate. This completes one refrigeration cycle. As this process continuously repeats, the evaporator continuously outputs chilled water for air conditioning or industrial cooling applications.
The aforesaid cycle occurs repeatedly to form a continuous heating process (Fig. 1-1).
2.2 Process Flow Diagram

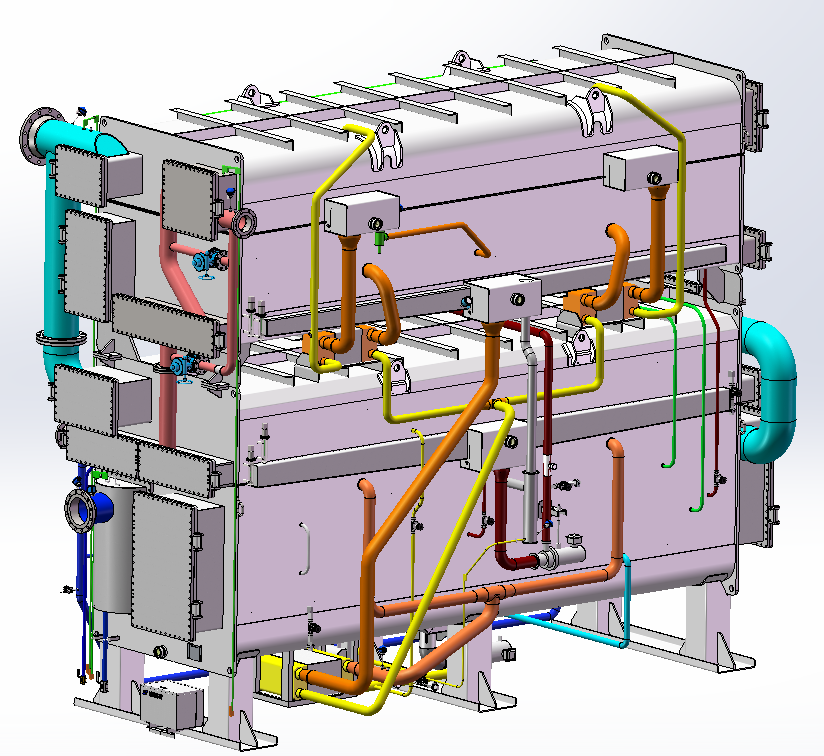
Fig. 1-1 Process Flow Diagram
2.3 Main Components and Functions
- Generator
Generation Function: The generator is the power source of the chiller. The heat source enters the generator and heats the diluted LiBr solution. Water in the diluted solution evaporates in the form of refrigerant steam and enters the condenser. Meanwhile, the diluted solution concentrates into a concentrated solution.
Featuring a shell-and-tube structure, the generator comprises the heat transfer tube, tube sheet, support plate, shell, steam box, water chamber and baffle plate. As the highest-pressure vessel inside the heat pump system, the generator has an internal vacuum approximate to zero (a micro negative-pressure).
2. Condenser
Condenser Function: The condenser is a heat generation unit. refrigerant steam from the generator enters the condenser and heats the DHW to a higher temperature. Then the heating effect is achieved. After refrigerant steam heats the DHW, it condenses in the form of refrigerant steam and enters the evaporator.
Featuring a shell-and-tube structure, the condenser comprises the heat transfer tube, tube sheet, support plate, shell, water storage tank and water chamber. Normally, the condenser and the generator are interconnected directly by pipes, so they have basically the same pressure.
3. Evaporator
Evaporator Function: The evaporator is a waste heat recovery unit. Refrigerant water from the condenser evaporates from the surface of the heat transfer tube, taking away the heat of and cools down the CHW inside the tube. Thus waste heat is recovered. refrigerant steam evaporating from the surface of the heat transfer tube enters the absorber.
Featuring a shell-and-tube structure, the evaporator comprises the heat transfer tube, tube sheet, support plate, shell, baffle plate, drip tray, sprinkler and water chamber. The working pressure of the evaporator is around 1/10 of the generator pressure.
4. Absorber
Absorber Function: The absorber is a heat generation unit. Refrigerant steam from the evaporator enters the absorber, where it is absorbed by the concentrated solution. The concentrated solution turns into a diluted solution, which is pump delivered into the next cycle. While the refrigerant steam is being absorbed by the concentrated solution, huge quantities of heat absorbed are produced and heat the DHW to a higher temperature. Thus the heating effect is achieved.
Featuring a shell-and-tube structure, the absorber comprises the heat transfer tube, tube sheet, support plate, shell, purging pipe, sprayer and water chamber. The absorber is the lowest-pressure vessel inside the heat pump system and is under the greatest impact from non-condensable air.
5. Heat Exchanger
Heat Exchanger Function: The heat exchanger is a waste heat recovery unit used to recover the heat in the LiBr solution. Heat in the concentrated solution is transferred by the heat exchanger to the diluted solution for thermal efficiency improvement.
Featuring a plate structure, the heat exchanger has a high thermal efficiency and a notable energy saving effect.
6. Automatic Air Purge System
System Function: The air purge system is ready to pump out the non-condensable air in the heat pump and maintain a high vacuum condition. During operation, the diluted solution flows at a high rate to produce a local low pressure zone around the ejector nozzle. Thus the non-condensable air is pumped out of the heat pump. The system operates simultaneously with the heat pump. While the heat pump is working, the automatic system helps maintain a high vacuum inside and ensure system performance and a maximized service life.
The air purge system is a system composed of the ejector, cooler, oil trap, air cylinder and valve.
7. Solution Pump
The solution pump is used to deliver the LiBr solution and secure the normal flow of liquid working mediums inside the heat pump.
The solution pump is a wholly-enclosed, canned centrifugal pump featuring zero liquid leakage, low noise, high explosion-proof performance, minimal maintenance and a long service life.
8. Refrigerant Pump
The refrigerant pump is used to deliver refrigerant water and ensure the normal spray of refrigerant water on the evaporator.
The refrigerant pump is a wholly-enclosed, canned centrifugal pump featuring zero liquid leakage, low noise, high explosion-proof performance, minimal maintenance and a long service life.
9. Vacuum Pump
The vacuum pump is used for vacuum purging at the start-up stage and air purging at the operation stage.
The vacuum pump features a rotary vane wheel. The button to its performance is vacuum oil management. The prevention of oil emulsification has an obviously positive impact on air purging performance and helps lengthen the service life.
10. Electric Cabinet
As the control center of the LiBr heat pump, the electrical cabinet houses the main controls and electrical components.
Waste Heat Recovery. Energy Conservation&Emission Reduction
It can be applied to recover LT waste hot water or LP steam in thermal power generation, oil drilling, petrochemical field, steel engineering, chemical processing field, etc. It can utilize river water, groundwater or other natural water source, converting LT hot water into HT hot water for the purpose of district heating or process heating.
Dual effect (Used for Cooling/Heating)
Driven by natural gas or steam, dual effect absorption heat pump can recover waste heat with very high efficiency (COP can reach 2.4). It is equipped with both heating and cooling function, especially applicable to concurrent heating/cooling demand.
Two Phase Absorption&Higher Temperature
Class II two phase absorption heat pump can improve waste hot water temperature to 80°C without other heat source.
Intelligent Control&Easy Operation
Fully automatic control, it can realize one-button On/Off, load regulation, solution concentration limit control and remote monitoring.
Artificial Intelligent Control System AI (V5.0)
■Fully-automatic control functions
The control system (AI, V5.0) is featured by powerful and complete functions, such as one-key start up/shutdown, timing on/off, mature safety protection system, multiple automatic adjustment, system interlock, expert system, human machine dialogue(multi languages), building automation interfaces, etc.
■Complete unit abnormality self-diagnosis and protection function
The control system (AI, V5.0) features 34 abnormality self-diagnosis&protection functions. Automatic steps will be taken by system according to level of an abnormality. This is intended to prevent accidents, minimize human labor and ensures a sustained, safe and stable operation of chiller.
■Unique load adjustment function
The control system (AI, V5.0) has a unique load adjustment function, which enables automatic adjustment of chiller output according to actual load. This function not only helps to reduce startup/shutdown time and dilution time, but also contributes to less idle work and energy consumption.
■Unique solution circulation volume control technology
The control system (AI, V5.0) employs an innovative ternary control technology to adjust solution circulation volume. Traditionally, only parameters of generator liquid level are used to control of solution circulation volume. This new technology combines merits of concentration&temperature of concentrated solution and liquid level in generator. Meanwhile, an advanced frequency-variable control technology is applied to solution pump to enable unit to achieve an optimal circulated solution volume. This technology improves operating efficiency and reduces startup time and energy consumption.
■Solution concentration control technology
The control system (AI, V5.0) uses a unique concentration control technology to enable real-time monitoring/control of concentration and volume of concentrated solution as well as hot water volume. This system can maintain chiller under safe and stable at high-concentration condition, improve chiller operating efficiency and prevent crystallization.
■Intelligent automatic air purge function
The control system (AI, V5.0) can realize real-time monitoring of vacuum condition and purge out the non-condensable air automatically.
■Unique dilution stop control
This control system (AI, V5.0) can control operation time of different pumps required for dilution operation according to concentrated solution concentration, ambient temperature and remaining refrigerant water volume. Therefore, an optimal concentration can be maintained for the chiller after shutdown. Crystallization is precluded and chiller re-start time is shortened.
■Working parameter management system
Through interface of this control system (AI, V5.0), operator can perform any of following operations for 12 critical parameters relating to chiller performance: real-time display, correction, setting. Records can be kept for historical operation events.
■Unit fault management system
If any prompt of occasional fault is displayed on operation interface, this control system(AI, V5.0) can locate and detail fault, propose a solution or trouble shooting guidance. Classification and statistical analyses of historical faults can be conducted to facilitate maintenance service provided by operators.